




The EATS trade-off
The latest category of heavy-duty engine oils were specifically designed to protect this latest generation of engines, but oil technology has not advanced far enough when it comes to optimizing and protecting the aftertreatment system, especially with regards to the diesel particulate filter (DPF). Consequently, fleet owners and operations managers have been forced to make a trade-off—one that requires more fuel.
How DPFs increase fuel consumption

DPF regeneration cycles
Once enough soot and ash accumulate, the engine initiates a
process where extremely high temperatures burn off the
collected particles to regenerate the DPF. Regen cycles can be
passive or active and both require additional fuel to run,
decreasing fuel economy.
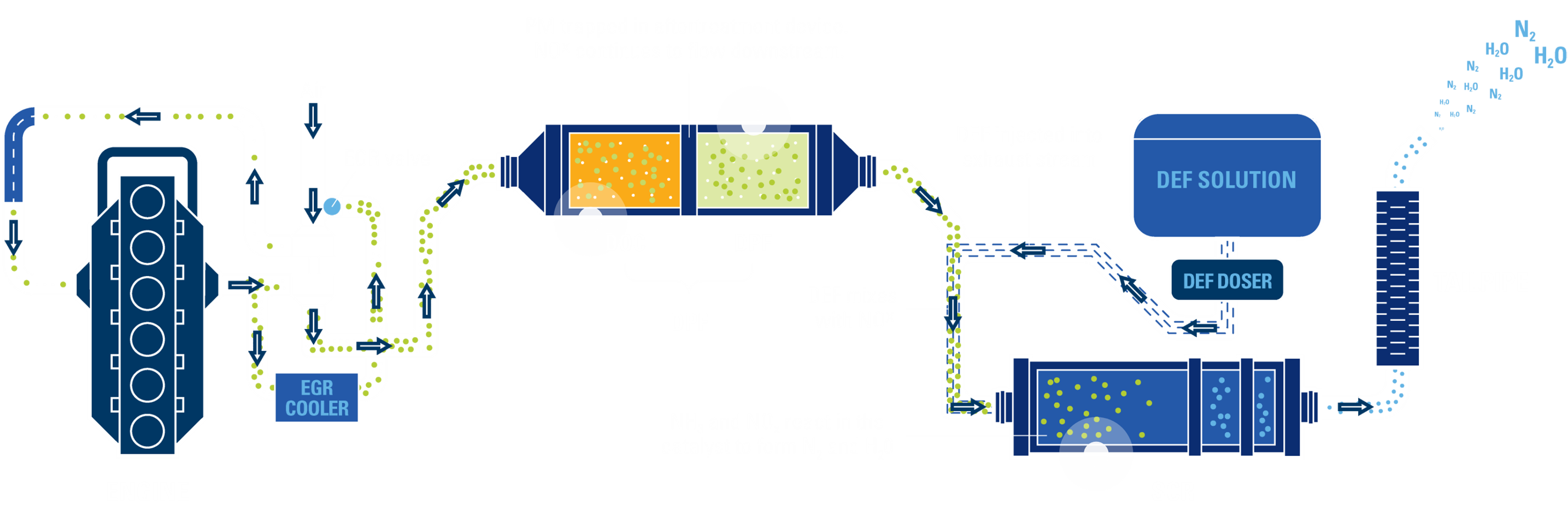
What's actually happening?
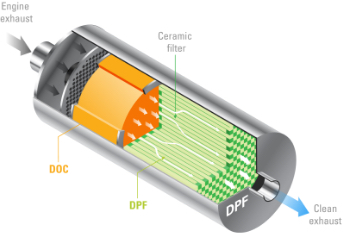
DPFs play a crucial role in cleaning diesel exhaust before it hits the tailpipe, reducing emissions of particulate matter (PM). As fuel burns, the DPF collects and stores up to 98% of incombustible particles in the form of ash and soot.
Ash clogging in the DPF
Soot burns off through regeneration, but ash remains in the DPF.
Engine lubricants contain metallic additives, such as anti-wear and
detergents, which clog the DPF and create backpressure. On top of
regeneration cycles, this backpressure puts additional strain on the
engine, causing a significant increase in fuel consumption.



Fueling fleets
Whether you operate a large fleet, a small fleet or
something in between, effectively managing fuel costs is
crucial to your business’s profitability. DPF clogging due
to ash buildup causes more frequent regenerations and
backpressure, which increases fuel consumption. And
those numbers can add up quickly across your fleet.


The DPF impact on
fuel economy
Take a deeper dive on how fuel efficiency is
negatively impacted by oil contaminant clogging
in DPFs.
Diesel Particulate Filter Operation
Learn how the DPF works, and what effect it has on fuel economy.


Inspecting the DPF
See how the honeycomb filter collects and stores
ash and soot to prevent harmful emissions.


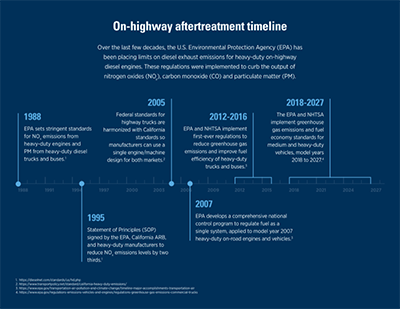
Cleaner air and lower-ash
lubricants
See how landmark legislation on air quality has
had a far-reaching impact on diesel engine
design, producing a need for lower-ash oils.


Maintenance issues and
aftertreatment systems
Understand the causes related to ash clogging in
your DPFs and why you may be servicing them
more than OEM guidelines suggest.


Clogged DPFs and the “Fuel
Penalty”
Is your engine burning fuel at a faster rate? It
may be because ash is clogging your DPF,
causing backpressure and forced regenerations.
Modal Component - Modals Configured




























